

Now you can select the newly created partition in the partition list and press OK:.Type “yes” and press Enter to confirm the write:.Finally select “Write” and press Enter to save the partition table to the disk:.Select the “Bootable” button and press Enter to mark the partition as bootable:.By default the new partition will cover the entire disk: Proceed with the size suggested by the partition utility.Select “Primary” to create a partition that can be used to store a bootable OS:.Select “New” to create a new partition:.In the boot menu select “Installation” and press Enter:.Finally press OK to save the settings and start the VM:.Go to the network settings and select either Host-only adapter (if you don’t have a local DHCP server) or Bridged mode (if your network has a DHCP server):.Specify the path to the Android image you downloaded.Go to the “Storage” tab, select the empty CD-ROM device and click the disc icon to browse for a disc image:.Click “Settings” to open the VM settings: Before you can start installing the Android OS into your VM, you need to mount the ISO file in it.The default value of 8GB should be enough for most cases: Finally you can customize the disk size.On the next page select “dynamically allocated”:.Proceed with the default virtual disk format:.
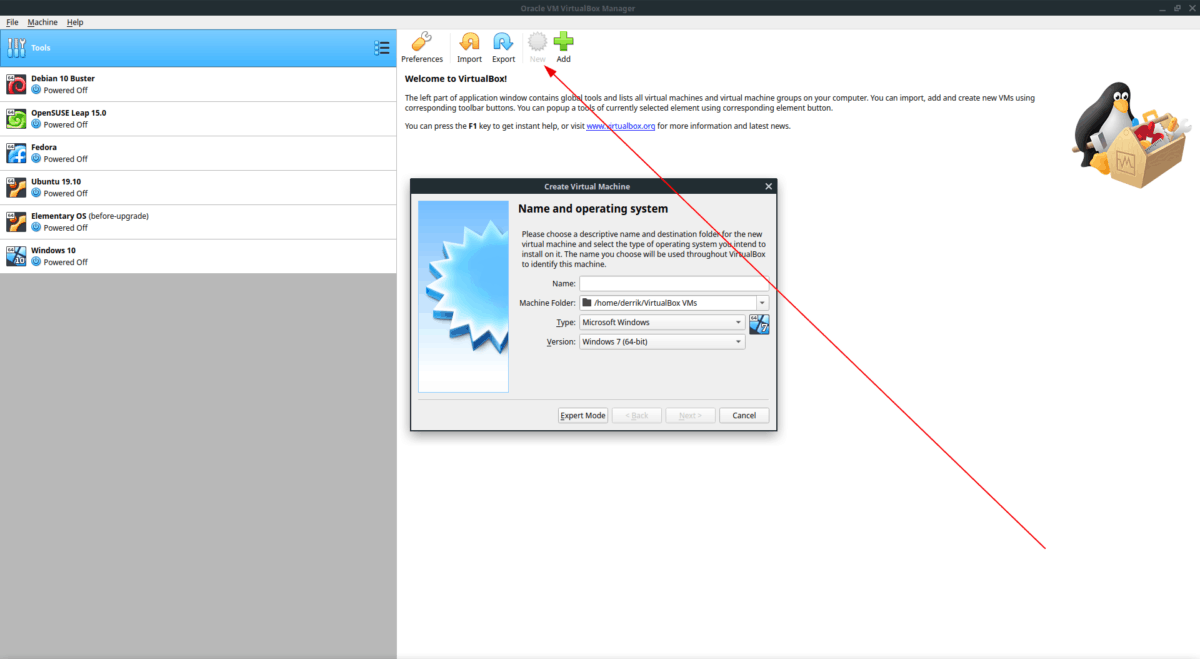
Select “Create a virtual hard disk now”:.Select “Linux -> Other Linux (32-bit)” as the machine type:.Click the “New” button to create a new VM: Before you begin, download the latest VirtualBox and get an x86 Android ISO from the website. We will show how to create an Android VirtualBox VM, configure it for debugging and use VisualGDB to debug the San-Angeles project. This tutorial shows how to use VirtualBox to accelerate debugging of Android apps with native components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
